Customized Manufacturing for Unparalleled Performance Forging Gears
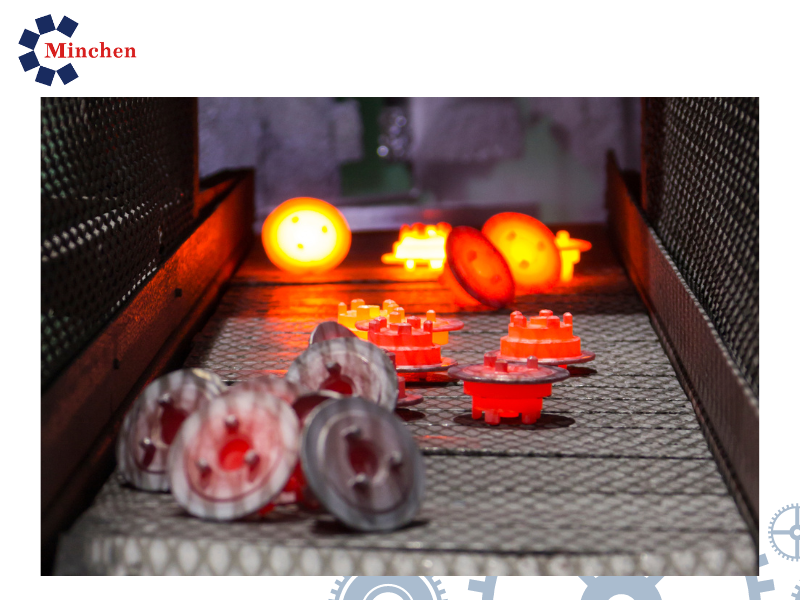
In the world of precision engineering and gear manufacturing, forging stands as a time-tested technique that combines craftsmanship and advanced technology. This article delves into the realm of forging gears, showcasing its benefits, customization possibilities, and the exceptional performance it brings to various industries.
what is the process of forging?
- Material Selection: The process begins with selecting the appropriate metal or alloy for the desired application. Different materials exhibit varying levels of ductility and suitability for forging.
- Heating: The selected metal is heated to a temperature that is below its melting point but high enough to make it more pliable. The specific temperature varies based on the material and the type of forging being performed.
- Preparation of Dies: Dies are specialized tooling components used to shape the heated metal into the desired form. Dies are made from high-strength materials, often tool steel, to withstand the forces and temperatures involved in the forging process.
- Placing the Workpiece: The heated metal, known as a billet or workpiece, is placed on the lower die in preparation for the forging process.
- Application of Force: The upper die is brought down onto the workpiece with immense force. This force, applied either through a mechanical press, hammer, or hydraulic press, causes the metal to deform and take the shape of the die cavities.
- Deformation and Flow: As the metal is subjected to compressive forces, it deforms and flows to fill the cavities of the dies. This plastic deformation leads to the desired shape and dimensions of the final product.
- Cooling: After the deformation process, the forged part is allowed to cool down slowly to room temperature. This controlled cooling helps prevent cracking and ensures optimal material properties.
- Trimming and Finishing: In some cases, excess material or flash may need to be trimmed or removed from the forged part. Further finishing processes such as machining, heat treatment, and surface treatments can also be applied to achieve the desired final characteristics.
Diverse Applications of Forging Gear
- Transmission Systems: Forging gears are commonly used in vehicle transmission systems. They help transfer power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring smooth acceleration and efficient power distribution.
- Differentials: Gears in differentials are subjected to high torque and varying loads. Forged gears excel in this application due to their strength and resistance to wear, enhancing the overall performance and lifespan of the vehicle.
Heavy Machinery and Industrial Equipment:
- Mining Equipment: Heavy machinery used in mining operations requires gears that can withstand extreme loads and harsh conditions. Forged gears provide the necessary strength and durability, ensuring reliable performance in mining equipment like crushers and loaders.
- Construction Machinery: Excavators, bulldozers, and other construction equipment rely on forging gears to handle heavy loads and repetitive stresses while maintaining precision in movement and operation.
Aerospace and Defense:
- Aircraft Engines: The aerospace industry demands gears that can operate under demanding conditions and maintain precision. Forging gears are used in aircraft engines to transmit power to various components, ensuring reliable and efficient propulsion.
- Helicopter Gearboxes: Helicopter transmissions require gears with high strength and resistance to fatigue due to the dynamic and complex nature of helicopter operations. Forging gears excel in this application.
Marine Propulsion:
- Marine Engines: Forged gears are integral to marine propulsion systems, transferring power from the engine to the propeller shaft. These gears must withstand the corrosive and high-torque marine environment while maintaining efficient performance.
Energy and Power Generation:
- Wind Turbines: The gearboxes in wind turbines require gears that can withstand varying wind conditions and loads. Forged gears provide the durability needed to ensure consistent energy generation.
- Power Plants: Forged gears are used in power plants for applications such as steam turbines and generators. The ability of forged gears to handle high temperatures and heavy loads is crucial in power generation.
Rail Transportation:
- Railway Systems: Gears used in railway systems, such as locomotives and railcars, need to endure rigorous operating conditions and provide reliable power transmission. Forging gears contribute to the safety and efficiency of rail transportation.
Oil and Gas Industry:
- Drilling Equipment: The oil and gas industry relies on gears for drilling equipment in challenging environments. Forged gears are chosen for their ability to withstand the extreme pressures and forces involved in drilling operations.
- Industrial Mixers: Mixing equipment in various industries requires gears that can handle heavy loads and ensure uniform mixing. Forged gears contribute to the efficiency and longevity of industrial mixing machinery.
The superior Strength and Durability of the forging process at Minchen
- Grain Structure Enhancement: During the forging process, the metal undergoes controlled deformation under elevated temperatures. This controlled deformation leads to the formation of a refined and aligned grain structure within the material. This aligned grain structure enhances the mechanical properties of the metal, including its strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance. The result is a gear that can withstand heavy loads and repetitive stress without premature failure.
- Material Choice: Minchen carefully selects high-quality materials with excellent mechanical properties for forging gear production. The choice of materials is crucial to achieving the desired strength and durability. Whether it's steel, alloy, or other specialized materials, the selection is made based on the specific requirements of the application.
- Precision Engineering: Minchen's expertise lies in precision engineering and design. The customization of gear profiles and shapes is done with meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that the final product meets or exceeds the required performance standards.
- Heat Treatment: After the forging process, Minchen often employs heat treatment techniques to further enhance the material properties. Heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering can significantly increase the hardness and strength of the forged gears while maintaining their ductility.
- Quality Control: Minchen places a strong emphasis on quality control throughout the entire forging process. Rigorous testing, inspection, and quality assurance procedures are in place to identify any defects or inconsistencies that might affect the strength and durability of the final products.
- Customization for Application: Minchen's customization approach ensures that each forged gear is tailored to the specific needs of the application. This customization involves choosing the right material, designing the optimal gear profile, and applying appropriate heat treatment methods to achieve the desired performance characteristics.
- Resistance to Fatigue: The controlled deformation and refined grain structure achieved through forging contribute to the gears' resistance to fatigue failure. This is particularly important in applications involving repetitive loading and cyclic stresses.
- Metallurgical Integrity: The forging process eliminates internal voids, porosity, and other defects that can compromise the material's integrity. This ensures that the gears maintain their strength and durability under challenging operating conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned what forging is and explored how it is used to create gear with superior strength and durability. Minchen has developed the technology necessary to complete these intricate processes at an extremely high-level. With their wide range of applications, it is clear why forging has been chosen worldwide as a reliable tool for creating quality tools and components. Not only is this form of metalworking centuries old, but it has become an integral part of many modern-day applications in today's world. Forging has proven time and time again its ability to withstand even the toughest conditions and remain a reliable source for fulfilling manufacturing needs going forward.
Contact us for your customization need!

